MILITARISM BEFORE WORLD WAR I
READ ABOUT IT!
Welcome to the Militarism before World War I Virtual Center. The first thing your group needs to do is read about militarism. After you read, you need to work together to complete the Militarism Center Page in your Lesson Chronicles.
The Arms Race
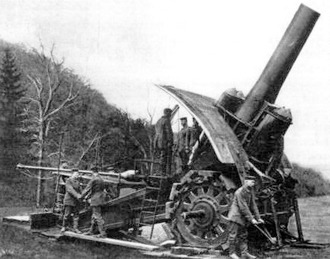 Big Bertha was the name given to this famous German Howitzer in World War I
Big Bertha was the name given to this famous German Howitzer in World War I
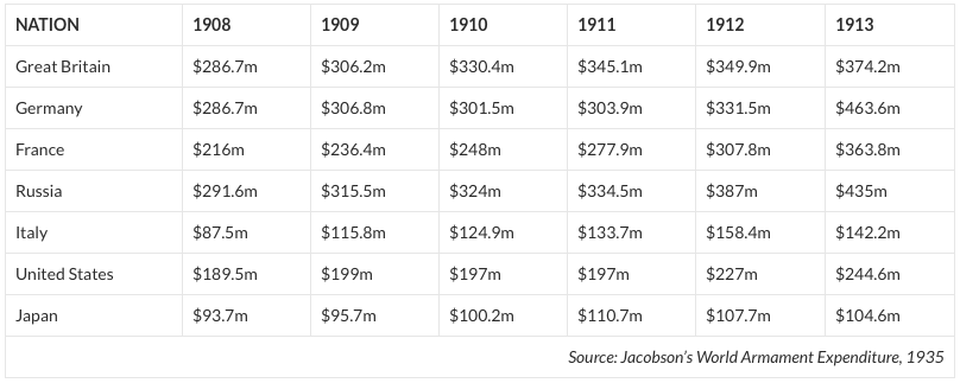
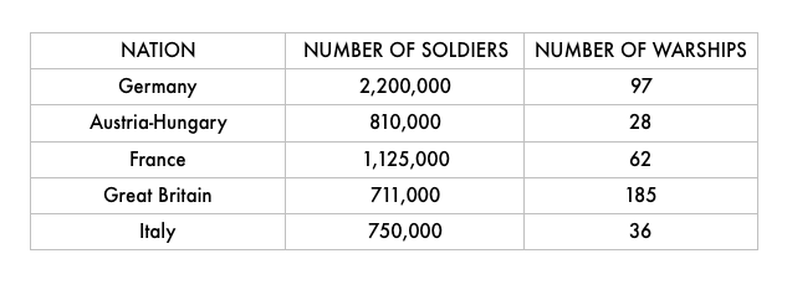
Military rivalry between nations also created an arms race. An arms race is a situation in which countries that are enemies each try to build or collect weapons faster than the other can. Before World War I, Nations competed to stockpile the most weapons.
The arms race was not just about the most weapons, it was also about the best weapons. Militarism inspired nations to invent new weapons technology and innovate old weapons to be more effective. Militaries all over Europe began adding new and improved battleships and submarines to their navies. Tanks and armored cars were invented for their armies. The invention of the airplane led nations to create the first air forces. There were great advancements made in the calibre, range, accuracy and portability of heavy artillery. Machine-guns, barbed wire, poison gas, torpedoes, mines, and grenades were all developed and put to military use.
The arms race was not just about the most weapons, it was also about the best weapons. Militarism inspired nations to invent new weapons technology and innovate old weapons to be more effective. Militaries all over Europe began adding new and improved battleships and submarines to their navies. Tanks and armored cars were invented for their armies. The invention of the airplane led nations to create the first air forces. There were great advancements made in the calibre, range, accuracy and portability of heavy artillery. Machine-guns, barbed wire, poison gas, torpedoes, mines, and grenades were all developed and put to military use.
British Militarism

Militarism before World War I really got its start in Great Britain. It was well known that Britain had the largest, most well trained, and equipped navy. Their navy had given them the opportunity to win 1/5 of the world as part of their vast empire. They were very well respected but they were also feared. All countries knew that if they ever had to face Britain’s navy, the chances of success would be very small. Britain worked hard to develop new technology to improve their navy and ships, research training techniques to produce the best navy soldiers, and recruit people to join the navy. Men in the navy were highly respected in Britain and abroad.
German Militarism

Militarism might have started in Britain but, militarism was strongest in Germany. Kaiser Wilhelm II was the ruler of Germany and the head of the German military. He was young and always worried about other nations taking him seriously as a leader. He was very competitive with the other rulers of Europe. He always wanted to be the best. He was jealous of the respect that Great Britain got from other nations for their mighty navy. He then became determined that the key to respect was a big military and other countries’ fear of that military. So Kaiser Wilhelm created tough training methods for his military officers. He encouraged the development of new weapons and modes of communication - and incorporated them into military strategies. He relied on a military council to help make decisions for the country and quit allowing the elected government officials a say in national affairs.
French Militarism

After losing the territories of Alsace and Lorraine to Germany in the Franco - Prussian War, France was angry with Germany. Their anger mostly came from fear. They saw Germany increasing the size of their military and investing large amounts of money in their military as well. France was worried about the Germans invading and taking even more of their land. So in October of 1910, the French Army Air Service was formed. France led the world in early aircraft design and by mid-1912 they had five squad of Army Air Servicemen. By 1914, the number of squads had grown to 132. France also doubled the amount of money it spent on its navy between 1910 and 1914.
Competition for the Best Navy

Britain and Germany were rivals for the best navy. Germany dramatically increased its navy by passing the Fleet Acts. The Fleet Acts increased the number of German cruisers from 9 to 12. In 1898, the German government ordered the construction of 17 new vessels. The Germans also pioneered the construction of military submarines: by 1914 the Kaiser’s navy had 29 operational U-boats.
In the meantime, Britain was working on its own ship building program. They had already established themselves as the best navy in the world. Now they worked to improve the technologies in their navy. The British introduced a new type of Battleship called the Dreadnought. It was larger, heavier, and faster than any other battleship and it was also lined with 12 inch guns.
In the meantime, Britain was working on its own ship building program. They had already established themselves as the best navy in the world. Now they worked to improve the technologies in their navy. The British introduced a new type of Battleship called the Dreadnought. It was larger, heavier, and faster than any other battleship and it was also lined with 12 inch guns.
Effects of Militarism

Militarism made nations feel invincible. National leaders used nationalism to promote militarism in their nations. Nations built up huge armies and navies and now they were hungry to use them. There were two major effects of militarism. Militarism allowed nations to develop the policy of imperialism. Imperialism is when a nation takes over another nation to rule them and take their natural resources. Militarism also created fear and excitement. Some nations feared war. Others wanted to go to war to prove their military power. Whether a nation feared war or wanted it, they new making friends would be the key to success. So militarism not only led to imperialism but it led nations for form alliances as well.
ANALYZE IT!
The second thing your group needs to do is to analyze what you have learned. Below, is a game. This game is not online (Sorry kids, the platform I used to use to create this game now costs money!). I will hand each table a game box. Listen to the following instructions as I read them aloud.
Building Forces Game
Today you will play a game called Building Forces to give you a better idea of militarism before World War I. In this game you will build up your military and weapons just like nations did before World War I.
Game Contents
Each game box needs to have the following contents. Check your box and make sure all the pieces are there.
1 Game Board
Game Instructions
- To begin, the world banker gives each player 1 army token, 1 navy token, 1 air force token, 1 technology token, and 1 weapons token.
- Each player chooses an Army Man moving piece.
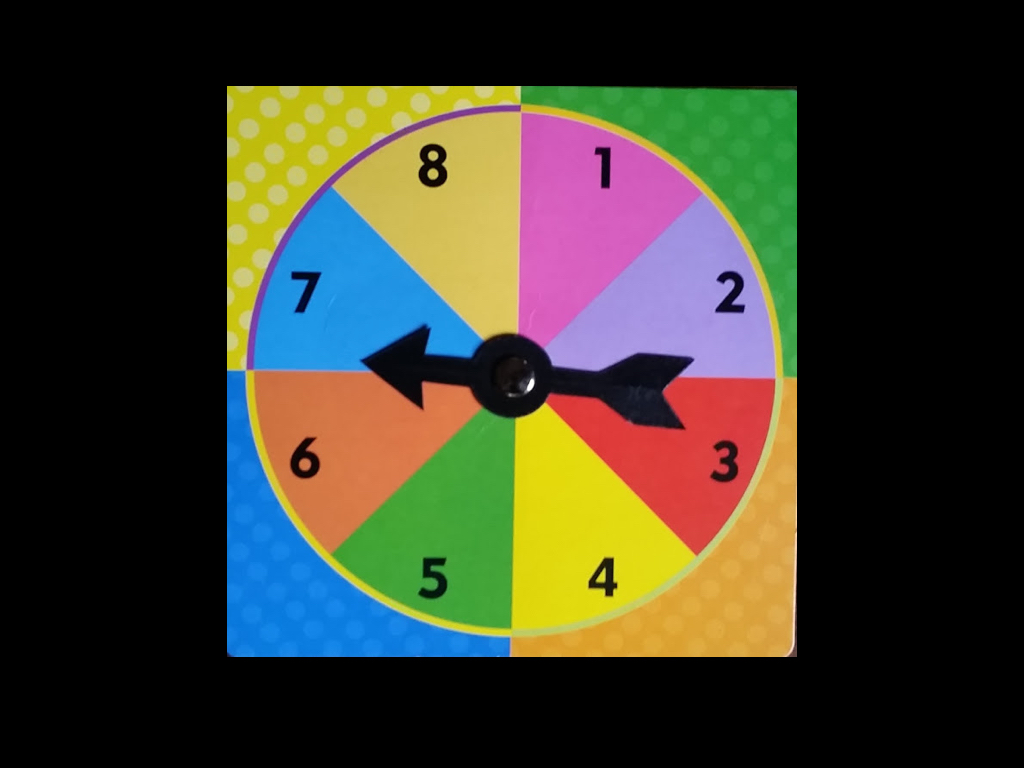
- Each player then spins the spinner. The game will begin with the player who spins the highest number and game play will move clockwise around the group.
- The player will spin the spinner and move that number of spaces.
- The player will do whatever the game board instructs them to do. If you land on a draw a breaking news card space, do so. Read the card and follow the instructions.
- If the player goes into debt the world banker will start that players debt card.
- The first player to get 5 army tokens, 5 navy tokens, 5 air force tokens, 5 technology tokens, and 5 weapons tokens wins the game.
PROVE IT!
You just learned about militarism before World War I and you analyzed the played a game where you worked to build up your military troops and arms. Now you need to show off what you know. Complete the Center Check by clicking on the Center Check Icon below and answering the questions.
CENTER COMPLETE!
You have completed the Militarism Before World War I Center. Click on the button below to go back to the Lesson 1 - The Causes of World War I Home Page.