UNIT 1: THE GILDED AGE
LESSON 2: BIG BUSINESS
FOCUS ACTIVITY
THE LESSON MISSION
|
Directions: Today's Amazing Race will focus on Big Business during the Gilded Age of U.S. History. Let's begin by focusing our attention on the Lesson Mission.
1. Write Big Business as the next entry in the Table of Contents of your Lesson Chronicles. 2. Open to Lesson 2: Big Business in your Lesson Chronicles. 3. Write your name and the date at the top of the page. 4. Write the title - Lesson 2: Big Business - on the title line. 5. Write the Lesson Mission under the Lesson Mission header. The Lesson Mission is: |
TEACHING ACTIVITY
CHALLENGE PREP - GUIDED READING

Today's race has five Challenges. Remember, each Challenge has a major objective called a Target. The Challenge Target is accomplished by completing a Challenge Activity. When you complete one Challenge Activity, you have met the Challenge Target. When you finish all 5 Challenges, you will have everything you need to answer your Lesson Mission Question so that you can complete your mission. We will start with a whole class Guided Reading. We will read as a class. The teacher will engage the students in pre-reading nonfiction text by identifying nonfiction text structures. Then, the teacher will help the students determine the main ideas and important vocabulary from each section. Finally, the teacher will ask questions to make sure that students understand the material.
The students will then use the reading and what they have learned to help their teams compete in the Amazing Race, meet each Challenge Target, and accomplish the Lesson Mission.
The students will then use the reading and what they have learned to help their teams compete in the Amazing Race, meet each Challenge Target, and accomplish the Lesson Mission.
BIG BUSINESS IN THE GILDED AGE
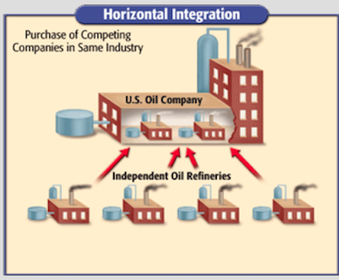
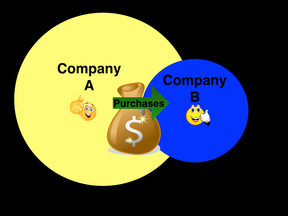
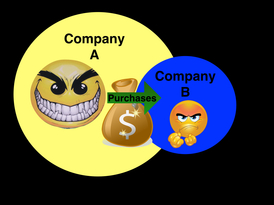
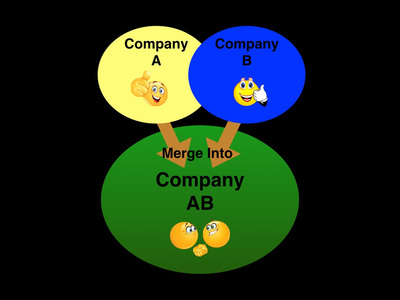
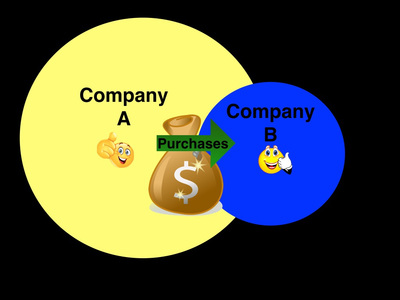
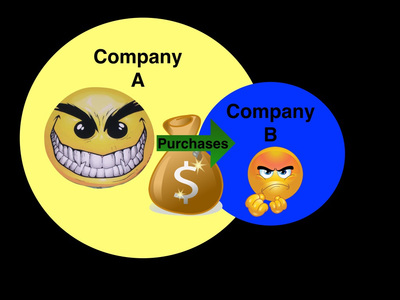
An acquisition is when one company purchases another company. An example of an acquisition is when AT&T bought Bell South in 2006. Sometimes a company does not want to be acquired, but is forced to in order to avoid bankruptcy. This type of acquisition is called a hostile takeover.
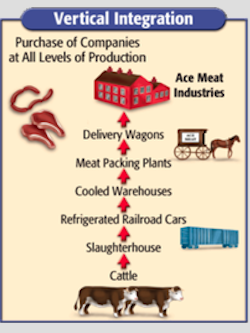
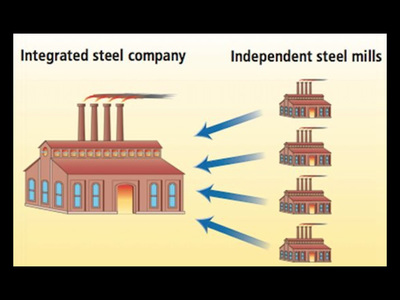
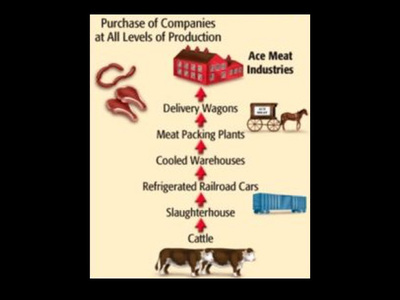
The second tactic was known as vertical integration. Vertical integration is when a company buys the companies needed to produce and transport the product in order to reduce costs. If Microsoft Xbox bought a plastics company, a silicone company, a circuit board company, and a trucking company, they would be able to produce and transport gaming consoles at cost which saves them a great deal of money.
When industrialists were able to lower the cost of making a product, they could lower the sale price of the product. In fact, they could sell their product at a much lower cost than other companies that sold the same product. This caused many of their competitors to go bankrupt or sell their business to avoid bankruptcy.
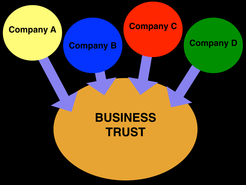
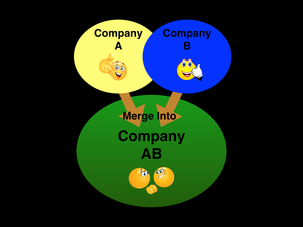
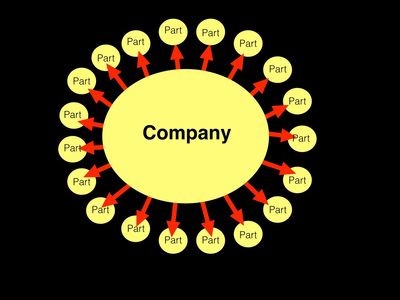
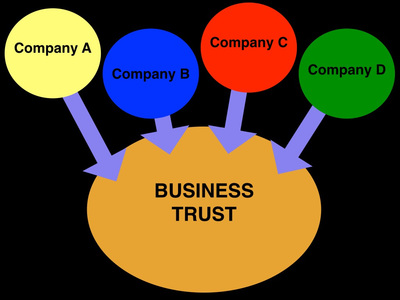
Sometimes big corporations within an industry would form trusts. Trusts were partnerships between big corporations in an industry that were made to strengthen their corporations' control over the market of their product. In these partnerships, the stocks of all the companies involved in the partnership combined and a group of people were selected to manage and control the combined stocks.
THE IMPACT OF BIG BUSINESS
|
Exxon-Mobil, Chevron, Shell, & BP are all part of the oil market.
|
All the business tactics that industrialists used to create corporations, grow in size, and expand all over the country were known as Big Business. Big business in America began with a network of railroads that connected the East to the West and cities to their natural resources. Big business grew when companies were able to expand westward and transport products all over the U.S. As businesses expanded, business owners formed corporations to raise the money they needed to grow and expand their industries. Big Business reached its peak when businessmen used vertical and horizontal integration tactics to form monopolies over entire industries and became industrialists. Big Business had a big impact on America's economy, politics, and society.
|
Capitalism
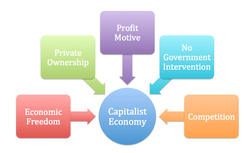
There are many different types of economies used in our world. The type of economy used in the U.S. is called capitalism. Capitalism is an economy in which a nation's trade and industry are controlled by private businessmen for profit, rather than by the government of the nation.
In nations with a capitalist economy, business owners are free to produce what they want and charge what they want without the government interfering. Today, Americans are still free to open businesses and make money, but there are more rules and regulations. These rules and regulations were a result of Big Business in the Gilded Age.
In nations with a capitalist economy, business owners are free to produce what they want and charge what they want without the government interfering. Today, Americans are still free to open businesses and make money, but there are more rules and regulations. These rules and regulations were a result of Big Business in the Gilded Age.
Wealth Distribution
|
|
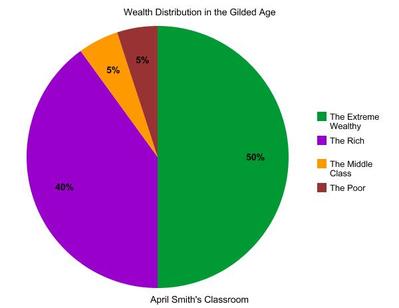
Big Business made a few men very rich during the Gilded Age. It was estimated that the most wealthy industrialists made up about 1% of the population in the United States, but they held almost 50% of America's wealth. The richest 2% through 9% held almost 40% of the nation's wealth. This means the middle class and poor who made up 90% of the population had to split the other half of the nation's wealth between them. 
There was a large gap in wealth between the rich and the poor. The way a nation's money is divided up between groups of people in a nation is called wealth distribution. During the Gilded Age, the U.S. economy was booming. Unfortunately, the wealthy 9% of the population in America were the ones benefiting from this economy.
|
THE AMAZING RACE
Welcome to the Lesson 2 - Big Business Amazing Race!
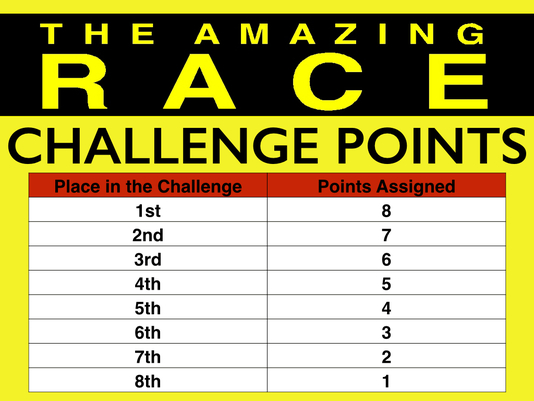
Today's Amazing Race has 5 Challenges. In the first Challenge, teams will race to play a game called Match 3 with the Vocabulary Words of the Lesson. In Challenge 2, teams will become Big Business Owners and race to find which of their companies are losing money and which are making the most profits in order to become the Big Business Winner! In Challenge 3, teams compete in the Stock Buyers Challenge where the team who has the most net worth at the end wins the Challenge. In Challenge 4, student teams compete to gain a real-estate monopoly by playing a Classic Game of Monopoly! In Challenge 5, student teams are expert economists who must present information on the Gilded Age Economy to the President using charts and graphs. Challenge placement is determined in different ways and is explained in each Challenge's directions. Placements receive the following points for the Challenge. The team with the most points wins the Lesson 2 Big Business - Amazing Race!
Challenge Points
LET'S GET STARTED...
|
Match 3
The Challenge 1 Activity is called Match 3. This race has three non-stop rounds. First, student teams will receive a game board. In Round 1, students will race to glue down all the vocabulary words in the first column of the game board in alphabetical order. When teams are done, they bring their board to the teacher station. The teacher checks it. If it is incorrect, the teacher shakes her head, “NO” and the team goes back to their table to find and fix their mistake. If it is correct, the teacher gives the team a set of definition cards.
In Round 2, teams work to match the definitions to the vocabulary cards. They will glue down definitions in the second column next to the word that it defines. When teams are done, they bring their board to the teacher station. The teacher checks it. If it is incorrect, the teacher shakes her head, “NO” and the team goes back to their table to find and fix their mistake. If it is correct, the teacher gives the team a set of picture cards. In Round 3, teams work to match picture representations to the vocabulary words and definitions that they represent. They will glue down pictures in the third column next to the word and definition that it describes. When teams are done, they bring their board to the teacher station. The teacher checks it. If it is incorrect, the teacher shakes her head, “NO” and the team goes back to their table to find and fix their mistake. If it is correct, the teacher gives the team their place in the race for Challenge 1! |
Match 3 Game Board
Match 3 Vocabulary Words
Match 3 Definitions
Match 3 Pictures
|
Show Me the Profit
The Challenge 2 Activity is called Show Me the Profit. In this Challenge, each team is an corporate accountant for a big business industrialist during the Gilded Age. The industrialists wants you to figure out which of his companies are making a profit and which ones are losing money. Teams will compete against each other to figure out each company's profits or losses. Then, teams must list the companies that are breaking even or losing money so that the industrialists can sell those companies off.
Teams will all receive an expense report that lists all the companies with their income and expenses. Students will subtract the expenses from the income to find the profit. When they have completed the expense reports for each company, they list the companies that need to be sold at the bottom of the report. When teams have completed their analysis, they will bring their expense report to the teacher station. The teacher checks it. If it is incorrect, the teacher shakes her head, “NO” and the team goes back to their table to find and fix their mistake. If it is correct, the teacher gives the team their place in the race for Challenge 2! |
Show Me the Profit Expense Report
|
Corporate Mogul
The Challenge 3 Activity is called Corporate Mogul. In this Challenge, each team is a big business industrialist. Each team plays the stock market and tries to have the most net worth at the end of the game. There are 8 companies in which students may purchase stock. Teams will discuss how many shares they want to buy in each company. When the stock exchange bell rings, the day begins. The teacher will draw event cards where companies stock goes up or down. When the bell rings again, the day ends. Each group will have the opportunity to sell their stocks or buy new stocks. When the last bell rings, the team that has the most money when their stocks are cashed out, wins first place. The team with the least amount will place 8th for this Challenge.
The game cards are not embedded below for this challenge, but you will not need these in your Lesson Chronicles. |
|
Monopoly
The Challenge 4 Activity is called Monopoly. In this Challenge, each team will play as one player in the game of Monopoly. Students try to buy up as much property as they can and develop the property to gain a real-estate monopoly. The team with the most property worth and wealth at the end of the class takes first place. The team with the least amount of points takes 8th place.
We will be playing using a downloaded computer app. If for any reason it does not work, we will play the old fashion board game! |
|
Spreading the Wealth
The Challenge 5 Activity is called Spreading the Wealth. In this Challenge, each team is a economic consulting firm hired by the President of the United States to present information about the economy in the Gilded Age. The president needs a quick, easy to understand presentation covering the nation's distribution of wealth, industries making the most money, net worth of the major industrialists, the average wages paid to industrial workers, and the amount of money donated by philanthropists.
Teams will compete against each other to create charts and graphs of information using information that your firm has gathered on each subject. Teams will receive an Economic Report with information about each of the topics above. You will need to organize the information into the different types of graphs for the president using an online graph maker called, Create a Graph. To begin, each team will get their first Economic Report on the first topic. Follow the directions to create a graph or chart with the information. Click on the icon that says CREATE A GRAPH to the left to get started. When you have completed the graph for the first information topic, click on print and save. When the graph comes up take a screen shot of the graph and save it to your desktop as Team# and Homeroom. For example, if I am Team 3 and I am in Mr. McNutt's Homeroom, I will save it as Team3McNutt. You will airdrop the teacher computer the graph your team saved. The teacher checks it. If it is incorrect, the teacher shakes her head, “NO” and the team goes back to Create a Graph to find their mistake and create another graph. If it is correct, the teacher gives them the next topic's Economic Report. Teams will follow this procedure until all 5 topics' Economic Report Graphs have been created correctly. The first team to complete all 5 correctly takes first place for Challenge 5. The team that completes all 5 correctly last, takes eighth place. |
Economic Reports
REFLECTION ACTIVITY

Directions: Now take a moment to think about all that you have learned in this lesson. What did you learn from all 5 Challenge Targets? Using PQA format, answer the Lesson Mission Question in your Lesson Chronicles using the information you gathered from the lesson. Remember, this helps me determine if you accomplished the mission by demonstrating that you understand how all the targets come together. When everyone is done, we will go over your answers as a class. You will be allowed to make corrections or add information that is shared by others. The Lesson Mission Question is below:
What were Big Business Practices in the Gilded Age of American History?
MISSION ACCOMPLISHED
MISSION CHECK

Directions: Did you accomplish your mission in Lesson 2? Well now it's time to prove it! Complete the Mission Check Activity below. You may use your Lesson Chronicles and the Lesson Page to help you. Remember to type your first and last name and check your answers before you submit. This is a graded activity worth 50 points. Click the Mission Check Button to begin the activity!
HOMEWORK
FAMILY DISCUSSION TIME
Remember, you have homework in Social Studies every night. Your homework is to tell your family what you learned in class today. This is an excellent way to keep a good line of communication open with your parents and it is a great way to make sure you are studying a little every night.
|