LESSON MISSION
LESSON READING
Raw Materials Start It All
Land and Resources
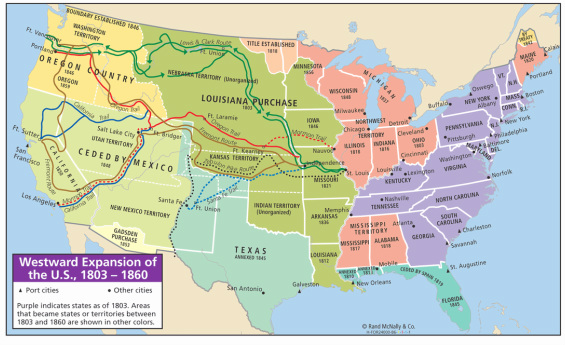
In the early 1800s, many Americans felt that the United States was destined to expand across the entire continent. This ideas was known as Manifest Destiny. Over the next few decades, the U.S. gained the land of the West in several different ways. The Louisiana Purchase was and still is considered to be the greatest real estate deal in history. The United States purchased the Louisiana Territory from France at a price of $15 million, or approximately four cents an acre. This doubled the size of the U.S. Soon, Texas joined the Union and the U.S. won California, Nevada, Utah, and parts of Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming from Mexico after the Mexican-American War. This increased the the size of the U.S. by twenty-five percent. In the Gadsden Purchase, the U.S. paid Mexico $10 million for the remaining parts of Arizona and New Mexico. The U.S. bought Alaska from Russia and annexed Hawaii.

All of this new land, and much of the land that had already been part of the United States in the first place, contained a wealth of natural resources. Natural Resources are things that are found in nature that are valuable to humans. Natural Resources led to industrialization because natural resources provided the raw materials used to build machines and factories, as well as the raw materials to manufacture goods.

Natural resources helped to bring about industrialization because they provided the raw materials for construction and production. Construction is the process of building something. Production is the process of making or growing something for sale or use. Raw materials are the basic materials used to build something or make a product for people to use. The United States had vast amounts of natural resources that provided raw materials for constructing factories and producing goods. These raw materials were minerals, animals, and plants and trees.
Minerals

First of all, America had a plethora of mineral resources which directly led to the mining industry. An industry is all the companies or factories that make a type of product. A mineral is any solid substance formed naturally under the ground. So, the mining industry were all the companies or mills that dug mines, which are pit or tunnels, in order to find and collect minerals and process them for use.

The mining industry really began with the California Gold Rush but few people truly struck it rich mining for gold. Ten years later, new deposits were gradually found throughout the West. Soon, silver was discovered in Pikes Peak, Colorado. Then, Nevada claimed Comstock Lode. Comstock Lode ended up being the largest silver strike in American history. Gold and silver were sought after mostly by individuals and families hoping to strike it rich.
Companies however, mainly focused on minerals that were needed by everyday people that could be found in large quantities. These minerals were coal, zinc, copper, limestone, iron ore, salt, and aluminum. All of these minerals were essential for American industrialization.
Companies however, mainly focused on minerals that were needed by everyday people that could be found in large quantities. These minerals were coal, zinc, copper, limestone, iron ore, salt, and aluminum. All of these minerals were essential for American industrialization.

Coal was mined primarily to produce energy and heat. Coal was eventually burned to generate electricity.

Zinc was primarily used for galvanizing steel and iron. Galvanizing means to cover steel or iron with a layer of zinc to prevent it from rusting. The iron and steel were then used to manufacture things such as railroad tracks and automobile frames.

Copper was used in the manufacture of brass and bronze. It more importantly was used to create copper wire. The copper wire was used to run electricity to homes, streets, and buildings; in automobiles and telephones; and eventually in all electronic appliances, tools and devices.

Limestone was used to make glass and cement. Cement was then used to construct everything from homes and sidewalks to bridges and skyscrapers and glass was used for windows and building decor.

Iron ore was used as the main construction metal for the railroads until people learned how to make steel out of iron ore. Steel was then used to make railroads, cars, subways, and ships, as well as in building construction, heavy equipment, appliances, power transmission turbines and towers.

Salt was used in the canned food industry to preserve the food and enhance the taste. Salt was also used to melt ice on the streets during the winter; in water treatment facilities; making paper and soap; and in petroleum refining.

Aluminum was used to make cans, aircraft, automobiles, and in electronic equipment and appliances.
Minerals provided the literal building blocks of industry. With these materials, Americans not only had items to produce for sale, but they also had raw materials to construct machines for faster and cheaper production; building materials to construct factories; and infrastructure materials to build cities. Infrastructure is the basic equipment and structures such as tunnels, roads, and bridges that are needed for a country or region to function properly.
Animals

The abundance of animals combined with the great amounts of land in which to keep the animals, contributed to the rise of the food production industry. The food production industry includes all the companies that grow plants and raise livestock; turn plants and animals into food; and package and distribute the food. Animals kept industrialization going as well. As more factories were built, industries developed. Industries needed workers. So immigrants from other countries poured into the U.S.to find jobs in industries. These immigrants worked in factories and had no time for farming or raising livestock. The food production industry provided a way to feed all the new people who weren't able to grow and raise food themselves. As the population grew, the food industry grew as well. Ranching, industrial livestock production, meat packing, and canning were all new industries that developed within the food production industry.

Ranching is the job of raising animals such as cattle, horses, and sheep on a large farm. When the U.S. gained the Southwestern States, it gained a very valuable resource - longhorn cattle. American farmers herded in and claimed the cattle and set up their own ranches. At first, beef was not popular so the animals were used for their skins and tallow. Tallow is animal fat used to make candles and soap. In the 1850s, railroads were constructed and ranchers began selling beef to Northern states where cattle were scarce. Soon, beef became very popular and its price rose making some ranchers quite wealthy, and establishing ranching as a new American industry.

When people think of ranching, most times they only think of raising cattle for beef. Cattle ranching was the biggest money maker in the ranching industry, but there were other ranches that specialized in other types of livestock as well. Livestock are farm animals that are kept, raised, and used by people. Dairy farms specialized in producing cow's milk. The cow's milk could be sold as milk or transformed into other dairy products such as sour cream and butter. Poultry farms specialized in raising chickens and turkeys for meat and eggs. Pig farms specialized in raising pigs for pork.
Plants and Trees

When the United States gained new land, they gained a variety of naturally growing plants as well as a variety of different soils for growing crops for farming. Farming is the process of growing crops. When farms began in the U.S., they produced a variety of crops used to support the farmer and his family. As towns developed, the farmer began growing enough to trade for services with merchants living in town. Eventually, farmers changed the way they planted altogether. Instead of planting different types of crops that would feed one family or a small town of people, they began planting large amounts of only one crop. Farmers planted corn, cotton, winter wheat, oats, corn, potatoes, sweet potatoes, peanuts, peas, and beans. When many farmers began to specialize in producing large amounts of only one crop, farming became an industry.

Food was not the only thing provided by plants. In the South, especially before the Civil War, cotton was the center of the Southern economy. An economy is the way in which a city, state, or nation makes and spends money. Before the Civil War, the money made in the South was mainly from farming and selling cotton to textile factories in the United States and to other countries around the world. After the Civil War, the South still farmed cotton, but they learned they could not make money on it alone. Soon, tobacco became a major cash crop as well. Wild plants were used in making medicines and eventually led to the pharmaceutical industry. Pharmaceuticals are the production and sale of medicine. When people began making medicines, some of the medicines were very harmful. It took a lot of research to determine which plants were beneficial and which were harmful.

Trees were another valuable resource. Trees led to the logging, lumber, paper, and tree fruit industries. The logging industry includes all companies that cut down trees to sell. The lumber industry includes all companies that processed trees into lumber. These industries made it possible to build homes, buildings, furniture, and boats. The paper industry includes all industries that converted lumber to paper. The tree fruit industry is any industry that harvested fruit from trees to sell.
When the United States gained massive amounts of land in the West, it gained a great deal of natural resources. An abundance of minerals, animals, plants, and trees put American on the track to industrialization; because they provided the raw materials needed to build industries and manufacture goods.
WHOLE GROUP ACTIVITY
Comprehension Check
As a class, we will read, discuss, and answer the following questions. You may take notes to help you with your Lesson Chronicles if you like, but notes are not required.
1. How did the United States gain so much land in the
1800s and early 1900s?
2. What are natural resources and how did they lead to
U.S. industrialization?
3. How did minerals contribute to building industries?
How did they contribute to producing goods?
4. What was ranching? Which type of ranching was the
biggest money maker during the Gilded Age?
5. What plants were used to produce goods? What
goods were produced with these plants?
SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY
Top That!
In this small group activity, you will play a game called, Top That!" In this game, each small group will look at each natural resource below. As a group, you will make a list of different ways that each natural resource contributed to industrialization. You will have 10 minutes to make a list for each resource. Really think through your list. Try to be original.
When time is called, each group will draw numbers to determine the order in which each group will participate. Whoever draws 1 will go first. Whoever draws 8 will go last. The group that goes first will give one of the items on their list. As each group takes a turn, they give one of the items on their list but cannot give an item that has already been listed. For every original idea you give, you get one point. I will compile a class list on the board. The group that has the most original and correct answers wins the game.
Natural Resources:
1. Limestone
2. Plants
3. Salt
4. Coal
5. Cattle
6. Trees
7. Iron Ore
8. Pigs
9. Zinc
10. Chickens
11. Copper
12. Land
When time is called, each group will draw numbers to determine the order in which each group will participate. Whoever draws 1 will go first. Whoever draws 8 will go last. The group that goes first will give one of the items on their list. As each group takes a turn, they give one of the items on their list but cannot give an item that has already been listed. For every original idea you give, you get one point. I will compile a class list on the board. The group that has the most original and correct answers wins the game.
Natural Resources:
1. Limestone
2. Plants
3. Salt
4. Coal
5. Cattle
6. Trees
7. Iron Ore
8. Pigs
9. Zinc
10. Chickens
11. Copper
12. Land
INDIVIDUAL ACTIVITY
Lesson Chronicles

- Enter this lesson into your Lesson Chronicles' Tables of Contents.
- Set up your entry for today's lesson by titling your paper and dating it.
- Write the Lesson Mission.
- Under the Lesson Mission, prove you have met today's mission goal by answering the following question in PQA format:
How did the abundance of natural resources in the United States led to industrialization?
Lesson Chronicles Table of Contents
1. Unit 1 Overview Lesson - The Gilded Age
2. Topic 1 Overview Lesson - Industrialization
3. Lesson 1 - The Factory System
4. Lesson 2 - Natural Resources Start It All
Your Name Today's Date
Lesson 2 - Natural Resources
Lesson Mission: I can describe how the abundance of natural resources in the United States led to industrialization.
The abundance of natural resources in the United States led to industrialization because__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.

Congratulations!
You have completed the Lesson 2 Lesson Module!
