Unit 3: We're Not Gonna Take It!
A Unit on the Progressive Era
A Unit on the Progressive Era
Lesson Module 19
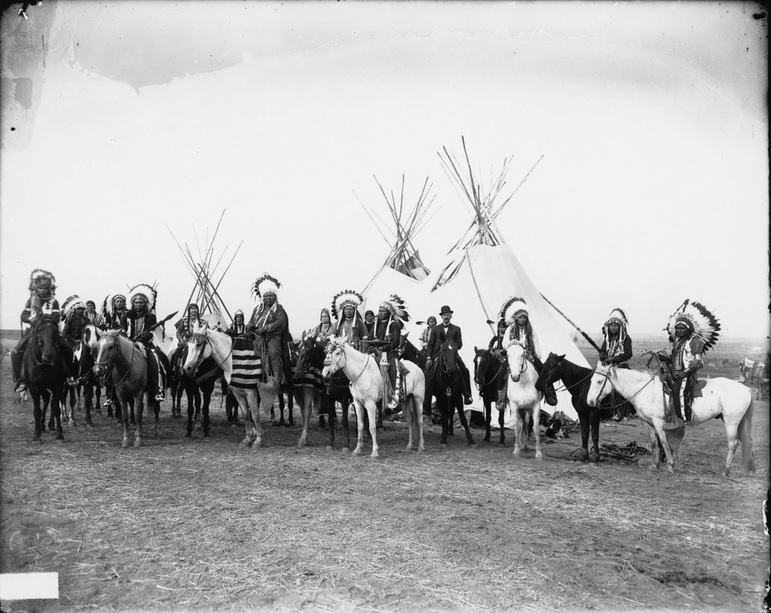
NATIVE AMERICANS
The Gilded Age & The Progressive Era
Focus Activity - Determining a Purpose for Reading
Lesson Outcomes

Outcomes are what you (the student) will be able to do after the lesson is over.
1. I can identify Native Americans as one of the oppressed groups of the Gilded Age.
2. I can describe the problems faced by the Native American people of the Gilded Age.
3. I can investigate how different Native American Progressives handled oppression and what they did to overcome oppression.
4. I can compare and contrast the results of different Native American Progressives' Efforts in overcoming oppression.
5. I can predict how different outcomes in Native American efforts to overcome oppression might have changed American History.
6. I can evaluate which Native American Progressive efforts I would have chosen to use and support my opinion with evidence.
1. I can identify Native Americans as one of the oppressed groups of the Gilded Age.
2. I can describe the problems faced by the Native American people of the Gilded Age.
3. I can investigate how different Native American Progressives handled oppression and what they did to overcome oppression.
4. I can compare and contrast the results of different Native American Progressives' Efforts in overcoming oppression.
5. I can predict how different outcomes in Native American efforts to overcome oppression might have changed American History.
6. I can evaluate which Native American Progressive efforts I would have chosen to use and support my opinion with evidence.
Lesson Mission
The lesson missions are the activities that you will complete to achieve the lesson outcomes. The missions for this lesson are:
Engagement Activity: Videoclip On the Plains Indians by the History Channel 0 Points
Teaching Activity: Native American Amazing Race Instructions 0 Points
Small Group Activity: Native American Amazing Race Challenge Organizer 100 Points
Whole Group Activity: Native American Trivial Pursuit 0 Points
Individual Activity: Pass Off Quiz for Lesson Module 19: Native American Rights - 100 Points
Teaching Activity: Native American Amazing Race Instructions 0 Points
Small Group Activity: Native American Amazing Race Challenge Organizer 100 Points
Whole Group Activity: Native American Trivial Pursuit 0 Points
Individual Activity: Pass Off Quiz for Lesson Module 19: Native American Rights - 100 Points
Engagement Activity - Introduction Video
We will watch the following video as a class. You may watch this on your own if you finish your work early or you may watch it at home. It might not be available using the school server. Sometimes videos even from Teacher Tube and the History Channel are blocked.
Teaching Activity - Understanding Native American Choices
|
Since first contact, Native Americans have been given three choices — which weren't really choices at all.
Assimilate The first “choice” was for a tribe to assimilate into the dominant American culture, become "civilized," give up tribal ways and be absorbed into America society. Many tribes tried this, many times through history. Education was the tool for assimilation in the boarding school experience. The government push to assimilate native tribes continued through the 1950s Urban Relocation Program. Relocate Even if a tribe, like the Cherokee, tried to join the American society, they could still be forced to relocate to Oklahoma Indian Territory hundreds of miles away. That's what happened on the Trail of Tears. Genocide Some tribes chose to fight or were forced to resist. While many have won some battles, they lost all the wars. Hundreds and thousands of Native Americans were killed in battles or by disease or starvation. One of the worst examples of genocide was what happened to the California tribes. Click here to go to the Interactive Map, where you will see how various tribes experienced assimilation, relocation or genocide during American history. Pbs.org. 2013. Indian Country Diaries . History . Assimilation, Relocation, Genocide | PBS. [online] Available at: http://www.pbs.org/indiancountry/history/assimilation.html [Accessed: 15 Dec 2013]. Small Group Activity - Native American Amazing RaceSo, which Native Americans fought and which ones assimilated? Which ones relocated or moved to reservations. In this activity, you will work as a small group to complete the Native American Amazing Race.
Each small group will race against each other and against the clock to gather information on several Native Americans who lived in the late 1800s and early 1900s. Each group will receive a challenge guide. You will have 20 minutes to collect and record the information asked for in the challenge guide. At that point time will be called. All pencils will be put down and you will receive your next set of instructions. To gather information, you will enter the Native American Portal below. The portal contains a page of icons. There is an icon for each Native American you will collect information on. Don't spend too much time on any one of these. You may divide and conquer but remember you only have one answer sheet for the whole group. You may begin.... NOW! Click on the Portal below to begin! Native American Progressives Graphic OrganizerA copy of the challenge guide is embedded below.
Whole Group Activity - Native American Trivial Pursuit!A slight change of plans. We will play Native American Jeopardy Instead!
Merry Christmas!
|
Tool BoxRemember, anything in the Tool Box could be on the Topic 2 test!
People To KnowAmerican Horse
Big Foot Black Elk Crazy Horse Dull Knife Little Wolf Red Cloud Sitting Bull Spotted Tail Standing Bear Susan LaFlesche Picotte Cochise Geronimo Joseph Black Kettle Ouray Quanah Parker Charles Alexander Eastman Little Crow Sarah Winnemucca Kaitchkona Winema Gall Amos Bad Heart Bull Gertrude Simmons Bonnin Plenty Coups Captain Jack Apache Kid Fred Waite Vocabulary To KnowAssimilate: to become "civilized," give up tribal ways and be absorbed into America society
Relocate: move to a new place Genocide: the deliberate killing of a large group of people, especially those of a particular ethnic group or nation Places To KnowThe American West
Events To KnowNov 29, 1864
Sand Creek Massacre US Cavalry led by Colonel John Chivington slaughter at least 150 Cheyenne and Arapaho (largely women and children) in what becomes known as the "Sand Creek Massacre" in Colorado Territory. Jan 7, 1865 Raid on Julesburg Cheyenne, Sioux, and Arapaho warriors raid and burn the town of Julesburg, Colorado in retaliation for the massacre at Sand Creek 39 days earlier. Jun 25, 1876 Custer's Last Stand Crazy Horse and Sitting Bull lead an army of Lakota, Cheyenne, and Arapaho Indians to a massive victory over General George Custer and the Seventh US Cavalry at the battle of Little Big Horn. Custer's force is part of an intended three-pronged assault against the Indian coalition that has harassed miners and homesteaders crossing their lands following the discovery of gold in the Black Hills in 1874. Partially because he badly underestimates the size of the Indian encampment along the Little Big Horn River, Custer chooses not to wait for the other units led by Generals John Gibbon and George Crook before launching his attack. Within hours, Custer and his entire detachment of 210 men are dead. Oct 6, 1879 Carlisle Indian School Richard Henry Pratt and Sarah Mather arrive at Carlisle, Pennsylvania with 82 Indian children recruited from the Dakota Territory for their new school. At the Carlisle Indian Industrial School, Pratt will implement his theories about education and assimilation, developed while earlier supervising 72 Indian prisoners at Fort Marion in St. Augustine, Florida. Feb 8, 1887 Dawes Severalty Act Congress enacts the Indian General Allotment Act, or Dawes Severalty Act, authorizing the president of the United States to carve existing Indians lands into 160 acre parcels to be distributed to individual Native American heads of households. "Surplus lands" (those remaining after individual allotments have been made) are to be purchased by the federal government and sold to Anglo-American homesteaders. Proceeds from these sales are to underwrite the "education and civilization" of the former Indian owners. Jan 1, 1899 Ghost Dance Wovoka experiences the mystical revelation that leads him to urge Indians to reform their lives and participate in the ritual of the Ghost Dance to prepare for the coming age of prosperity and peace. Dec 15, 1890 Murder of Sitting Bull Sioux chief Sitting Bull is killed by Indian police attempting to arrest him under orders from the territorial Indian agent, who fears that the hero of the Little Big Horn will unite Indians incited by the Ghost Dance to launch a war against white settlements and federal authority in the Dakota Territory. In the aftermath, Sitting Bull's followers flee the camp to seek protection under Chief Red Cloud at the Pine Ridge Agency. Dec 29, 1890 Wounded Knee Massacre Having intercepted Sitting Bull's followers the previous day, a battalion of the Seventh Cavalry opens fire on the Sioux camp on the Wounded Knee Creek, killing 300 people—two-thirds of them women and children. The "Wounded Knee Massacre" effectively marks the end of armed Indian resistance to white western expansion in the nineteenth century. Oct 16, 1911 Society of American Indians The Society of American Indians is founded at Columbus, Ohio. Graduates from the Carlisle School, the Indian Industrial Training School at Haskell, and the Hampton Institute play prominent roles in founding this organization dedicated to advancing educational opportunities for Native Americans and establishing a voice for Indians in American politics. The organization argues that to achieve these objectives, Indians must begin to look beyond tribal identities and local concerns in order to advance their common national interests. Sep 20, 1932 Death of Wovoka Jack Wilson dies in Yerington, Nevada. As Wovoka, Wilson led the revival of the Ghost Dance in 1890, a spiritual and political movement leading to the Massacre at Wounded Knee. |