LESSON 11:
THE GEOGRAPHY OF THE MIDWEST
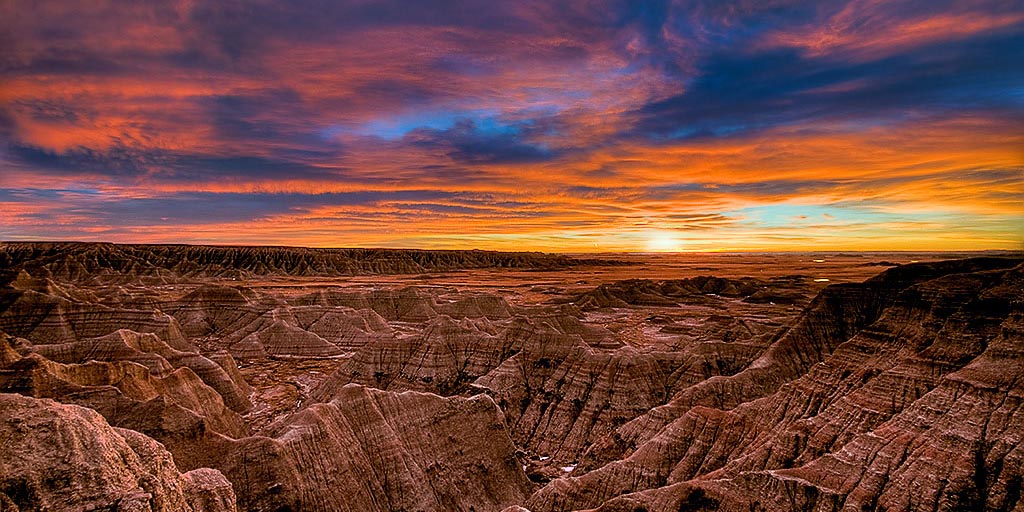
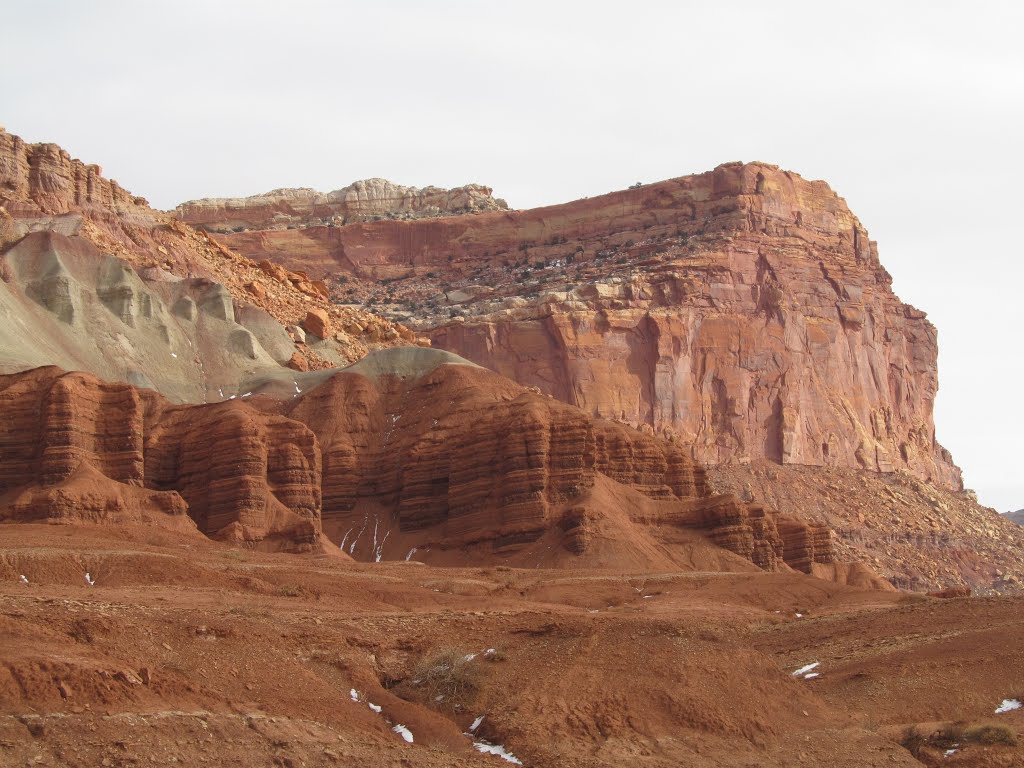
 The Badlands
The Badlands
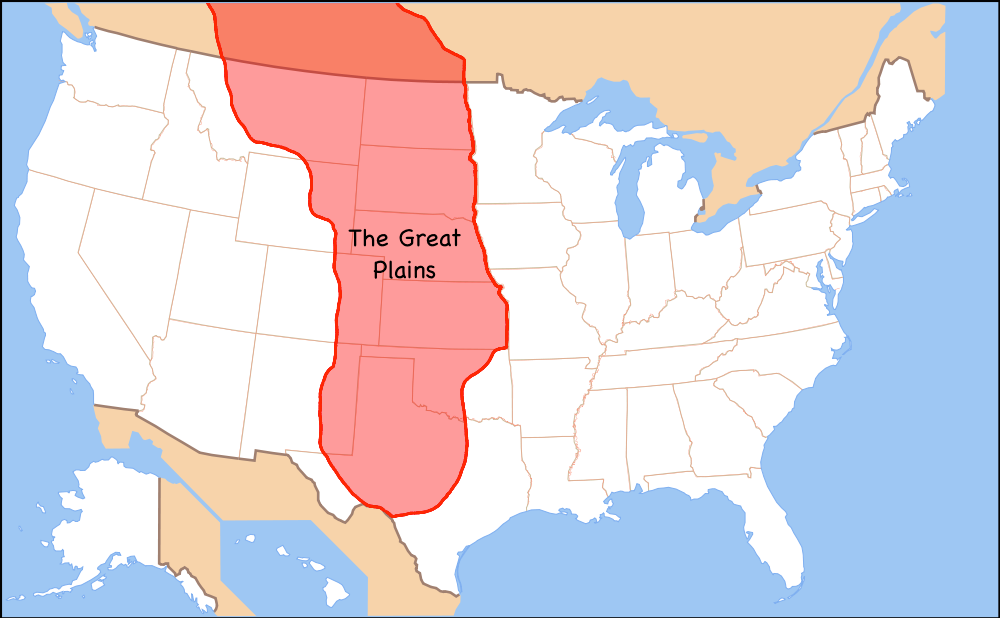
There are areas of the Great Plains that are very dry. These areas are called the Badlands. If you visit the Badlands, you will notice its hilly dry land. Within its steep cliffs, people have found fossils. Some of these fossils have belonged to dinosaurs like the Tyrannosaurus Rex. Of course, when these reptiles roamed the Earth, the climate was much wetter. Located in this area is the Badlands National Park in South Dakota.
 Tyrannosaurus Rex Bones
Tyrannosaurus Rex Bones
The dry land and cliffs have been changed during the last millions of years. They have been eroded by wind, rain, sand, and water. This is why the Badlands have canyons. Their sides are very steep with rocks that are rough. Nature wears away the layers of these rocks. This allows the soft rock to be shaped, stripped, and molded over time. Although the Badlands is a dry region, people visit to see its beautiful landscape. Its cliffs and rock are still being eroded today. In fact, you can tell that erosion is taking place because fossils are still found in the area.
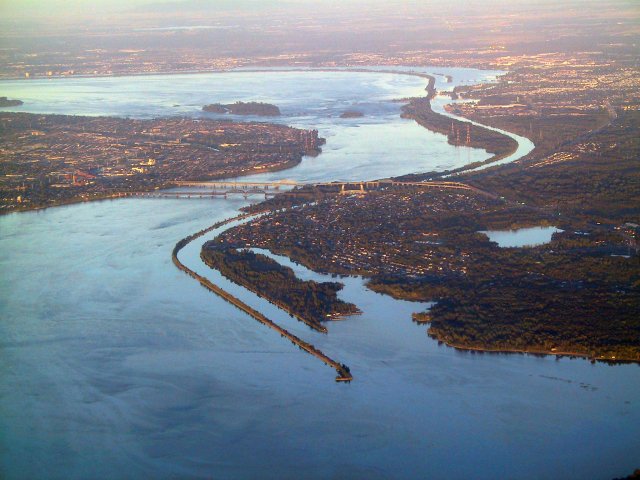
Lakes and Rivers
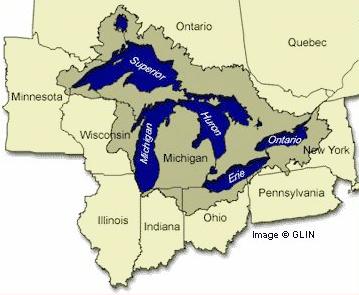
 An Aerial View of the Great Lakes
An Aerial View of the Great Lakes
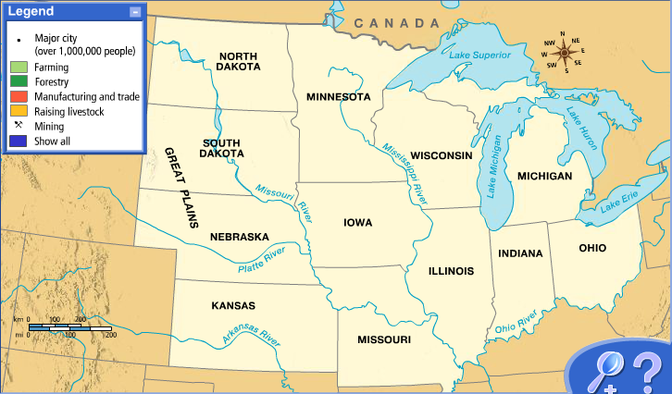
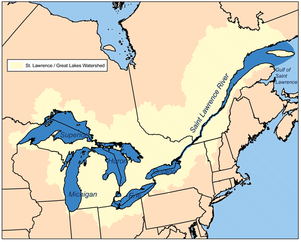
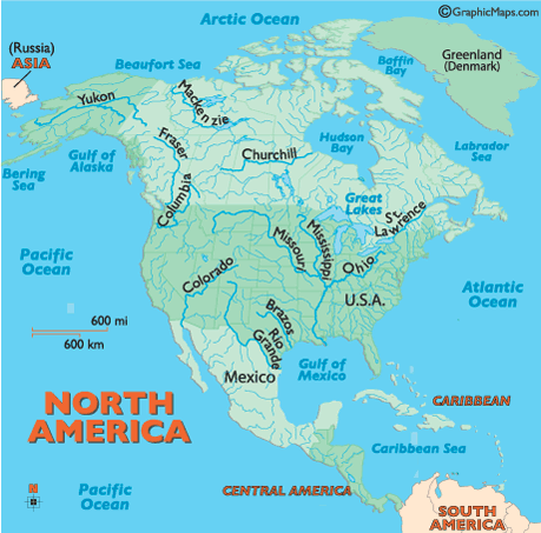
The water in the Midwest is very important. The region's rivers and lakes provide waterways for transportation and water for drinking and crops. The Great Lakes are a few of the region's important waterways. These freshwater lakes are connected to each other and the St. Lawrence Waterway.
How They Got There
The lakes were formed long ago during the Ice Age. Glaciers covered most of North America. As they moved, they changed the land. Huge, deep pits were left behind. Melting glacier water filled these pits. Now we have the largest group of freshwater lakes in the world. The St. Lawrence Waterway or Seaway connects the lakes to the St. Lawrence River. The river then flows into the Atlantic Ocean, so ships can reach the Midwest through these Great Lakes.
Uses
There are also canals in this region. Remember, canals are dug across land to connect larger bodies of water. This allows ships to travel from larger bodies of water to smaller bodies of water. In Illinois there is the Illinois Waterway. It has many canals and rivers. Lake Michigan is connected to the Mississippi River by this waterway. Once it reaches the Mississippi River, the water flows into the Gulf of Mexico.
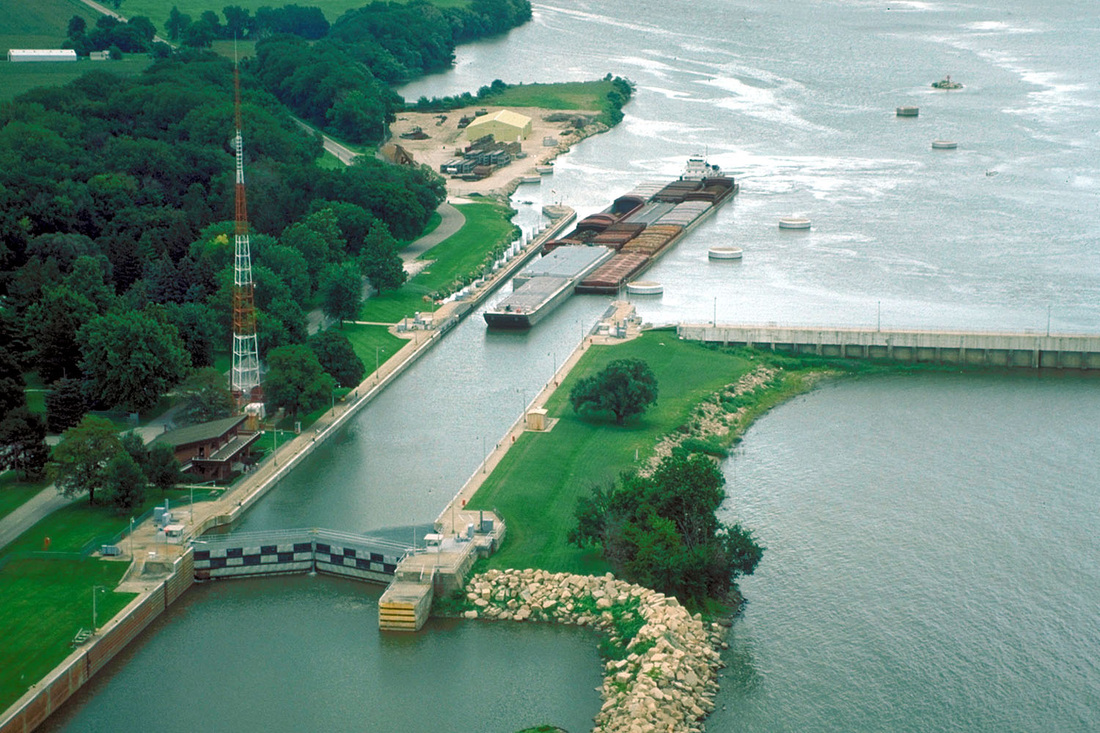
Lakes
Even though the Midwest has level land, some of its waterways are not level. There are parts of the Great Lakes that have different levels of water. It used to be difficult for ships to sail through these lakes. The key came when locks were invented. Locks are very large structures that can raise and lower ships. They would raise or lower the ships between different levels of water. If you visit Lake Erie and Lake Ontario, you will see the Welland Ship Canal. This canal helps to connect Lake Erie and Lake Ontario.
Rivers
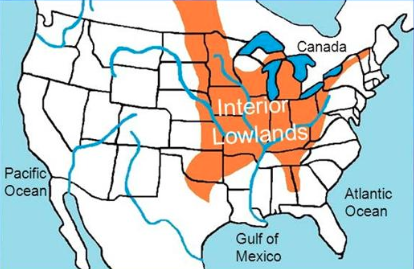
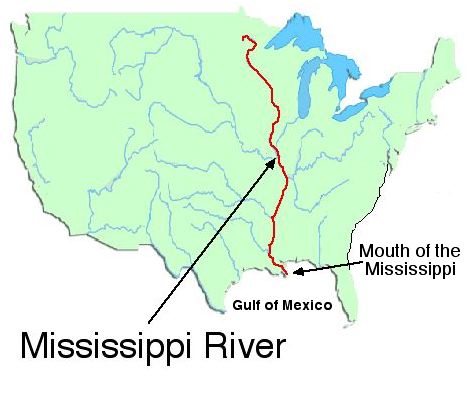
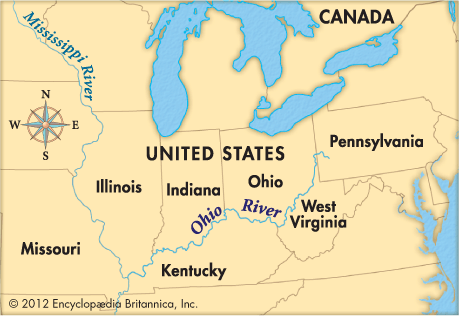
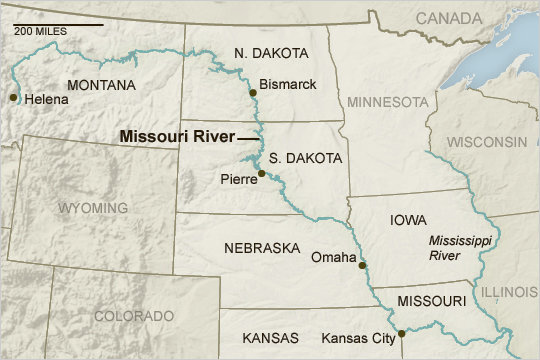
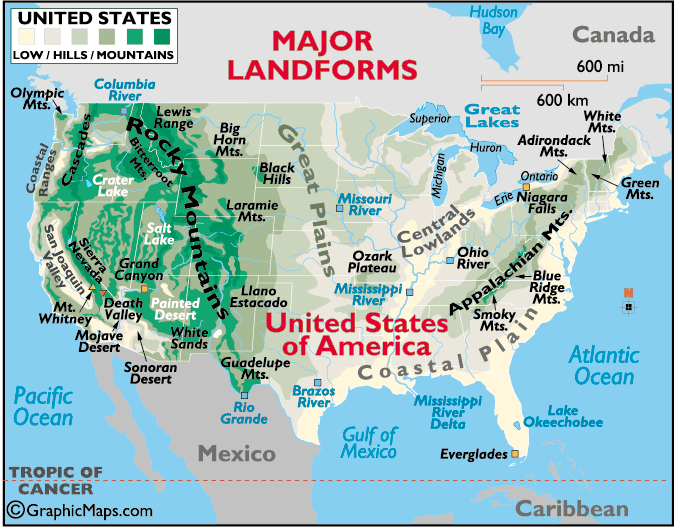
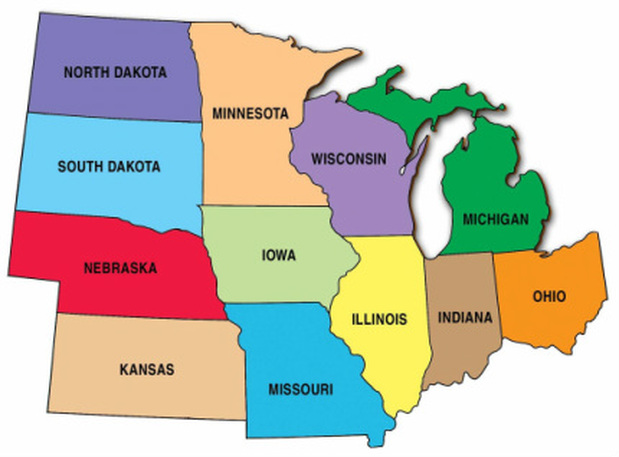
The region also has some of our country's important rivers. The Mississippi River begins in Minnesota. If you look at a physical map, you will notice that it borders five states in the region. The Ohio River starts in the Interior Lowlands. Starting in Ohio, this river flows along the southern border of Indiana. It also flows along the southern edge of Illinois. This is where it meets the Mississippi River. Another important river is the Missouri River. You probably think it begins in Missouri. Well, it actually begins in Montana. This river flows through six of the region's twelve states. It meets the Mississippi River near St. Louis, Missouri.
Climate
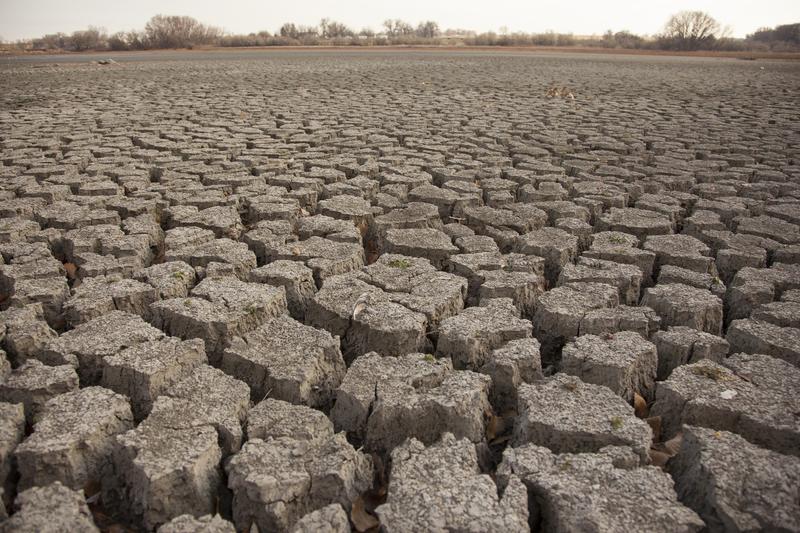
The Midwest's climate is very important to its economy. Most of our country's farms are located in this region. This area of the U.S. is not near the Pacific or Atlantic Oceans. Therefore, the Midwest has very hot summers. In fact, places that are located in the middle of continents tend to become hotter more quickly during the summer. Winters are also very cold on the plains. The eastern part of the region receives more rain than the Great Plains. The rain is so little in the Great Plains, farmers have to use irrigation to water their crops. They bring in water, through pipes, from nearby rivers and lakes. They also drill wells to get water from underground. Due to the low amount of rain, there have been droughts in the Great Plains. Droughts are long periods of time where there is no rain or very little rain.
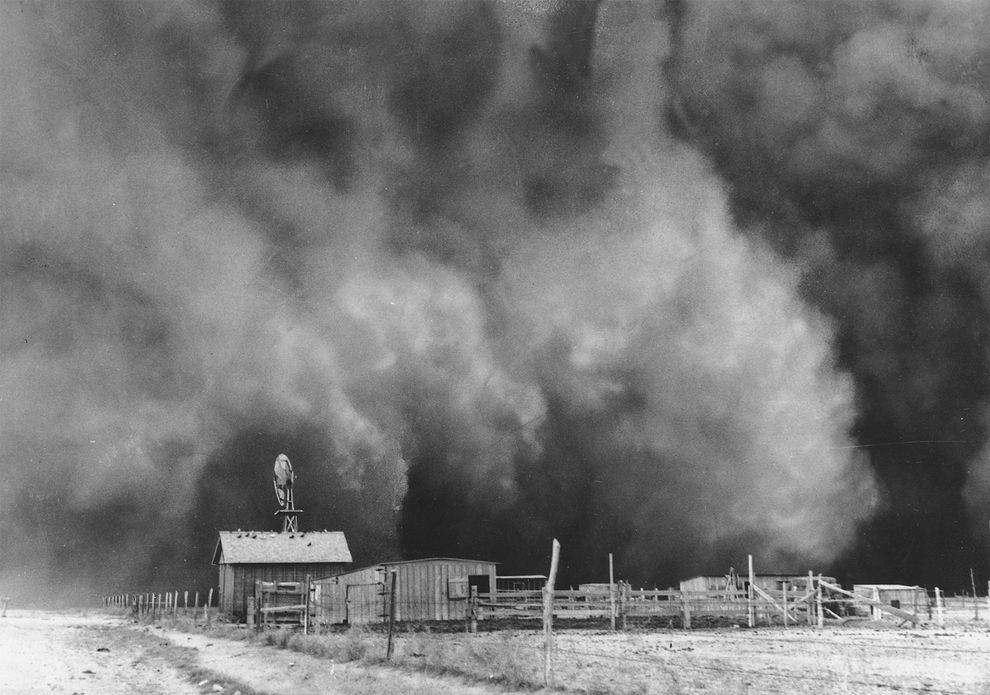
When there is a drought or very little rain, the soil can be damaged. During the 1930's this happened. The Great Plains received so little rain at the time, a drought occurred. This drought turned the soil in the fields and pastures to dust. Once this happened, the Great Plains was called the Dust Bowl. Imagine, wind blowing soil all around the Great Plains. The wind even carried the dust as far as Washington, D.C. The wind was eroding the soil that was on the plains. This made the fields less fertile or able to grow crops. Fortunately, the drought ended.
As you will read later, the region's climate and physical features are very important. They have made the Midwest one of the largest farming areas in our country.
As you will read later, the region's climate and physical features are very important. They have made the Midwest one of the largest farming areas in our country.
SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY
Mapping

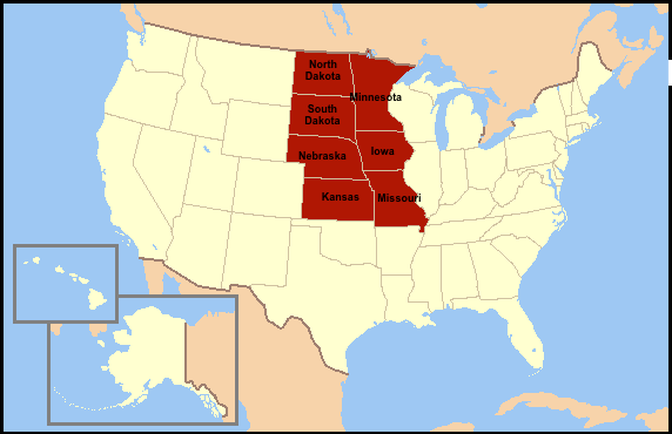
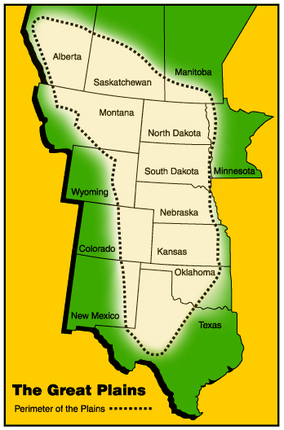
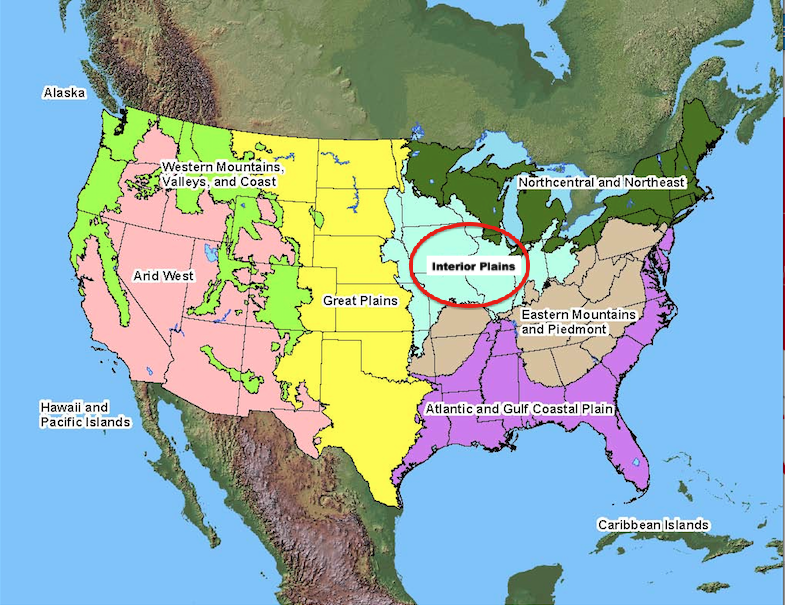
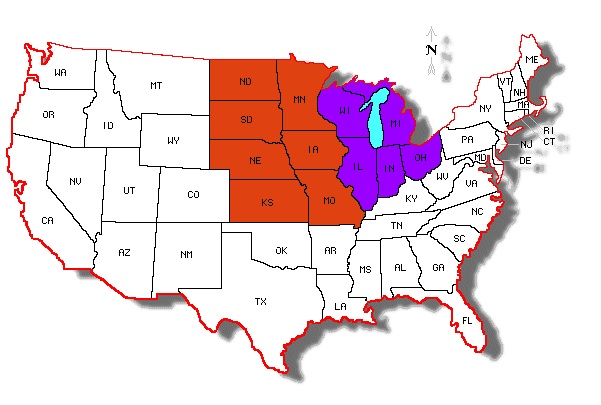
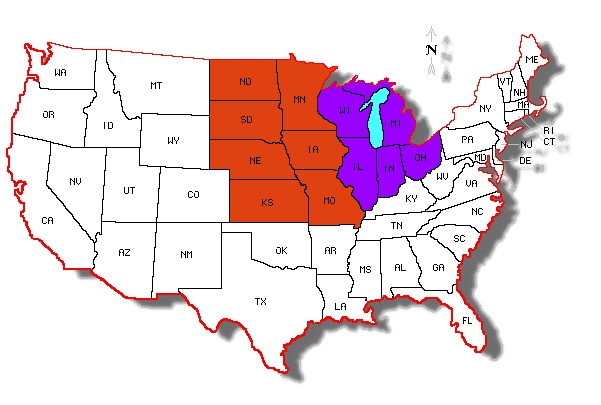
DIRECTIONS: Over the next few lessons, you will work on a geography project. You will each make your very own, geography picture book that will go into your Lesson Chronicles. You will each receive a photocopy of the packet embedded below. You can find all the answers on this webpage. There are more maps below these instructions and above the embedded packet to help you.
INDIVIDUAL ACTIVITY
Lesson Chronicles
Remember you will do the Geography Packet as your Lesson Chronicles Entries for Topic 6.

DIRECTIONS: Make sure that you have put all of the mini-project pages into your lesson chronicles. You will be graded on this mini-project. It will be worth 100 points.
HOMEWORK
Family Time

Remember, you have homework every night in Social Studies. Your homework is to show your Lesson Chronicles to your family and tell them what you learned today. Not only will this give you quality time with your family but it will help you review for your unit test. Go over your lesson chronicles entry from today everyday to help you study for the Topic Quiz and Unit Test.
END OF LESSON 11 MODULE

Congratulations! You have completed Lesson 11 Module!