THE LESSON 1 MISSION
By the end of Lesson 1, you should be able to say:
- I can explain why we have night and day on Earth.
- I can explain how light and dark play a part in creating the phases of the moon.
- I can illustrate how shadows are formed and explain why shadows form the way they do.
LESSON 1: THE SCIENCE OF ART
 Leonardo DaVinci
Leonardo DaVinci
Leonardo DaVinci was the great artist that created famous artworks like, The Mona Lisa and the Last Supper. He said, “To develop a complete mind: Study the science of art; Study the art of science. Learn how to see. Realize that everything connects to everything else.”
He makes a very good point in this quote. Science is a part of art. Light and dark, shades of color, and even the materials we use to create visual art are all a product of science. The music we make is also a science. From the way we produce sounds in music to the way we hear these sounds is all explained by science.
In turn, science can't exist without art. The arts force us to ask questions and they evoke our curiosity. We use science to answer questions and satisfy our curiosities.
He makes a very good point in this quote. Science is a part of art. Light and dark, shades of color, and even the materials we use to create visual art are all a product of science. The music we make is also a science. From the way we produce sounds in music to the way we hear these sounds is all explained by science.
In turn, science can't exist without art. The arts force us to ask questions and they evoke our curiosity. We use science to answer questions and satisfy our curiosities.
THE EARTH'S PLACE IN THE UNIVERSE

Let's explore this idea. Artists use techniques based on science to create the perception of light and shadows. Let's explore the science behind creating light and shadows in art by recalling Earth's place in our solar system.
EXPLORING THE SCIENCE OF LIGHT
|
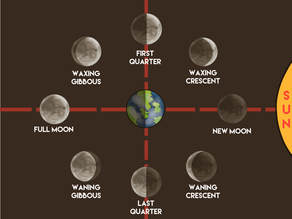
The sun lights up the side of the moon that faces it. Put your math caps on... the angle of light cast on the moon changes as the moon orbits around the Earth. Over the 28 days it takes the moon to orbit the Earth, the sun produces different angles of light on the moon depending on where the moon is in orbit. These angles are called the phases of the moon. The moon reflects light from the sun. As the moon orbits Earth, Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the moon, making part of the moon dark. The side of the moon that does not face the sun at all is always dark. So darkness occurs when there is no light or something is blocking the light.
Click on the link below to participate in an interactive that explains how this works.
|
EXPLORING THE SCIENCE OF SHADOWS
|
Now let's focus on how light and the blocking of light produces shadows. You might not always notice it, but when you're in the sun, your shadow is often nearby. It may be in front of you or behind you. Or it may be to your side. Wherever it is, your shadow looks like you and moves like you. Two things are needed to make a shadow. The first is light. The second is something that blocks the light. Together, these two things make an area that is darker than what is around it. This area is called a shadow.
Outside, people make shadows when they block light from the sun. Think about what happens when the sun is behind you. Your body blocks some of the sun's light, causing a shadow to form in front of you. The shadow takes on the shape of your body. When the sun is in front of you, the shadow forms behind you. If the sun is to your left, then the shadow forms to your right. If the sun is to your right, then the shadow forms to your left.
|
Other things make shadows, too. Clouds make shadows when they pass in front of the sun. A baseball cap makes a shadow on your face. Trees and buildings make shadows. Any object exposed to the sun can create a shadow
|
Shadows come in many sizes. A small person makes a small shadow. A big building makes a big shadow. The position of the sun affects the size of a shadow. A person or object blocks more light when the sun is low in the sky. More blocked light makes shadows longer. Less light is blocked when the sun is high in the sky. This makes shadows shorter.
The night sky is simply a very large shadow. The sky turns dark when your part of Earth spins away from the sun. Earth blocks the sun's light from reaching the sky above you. No light means no heat. That's why nights are almost always cooler than days.
|
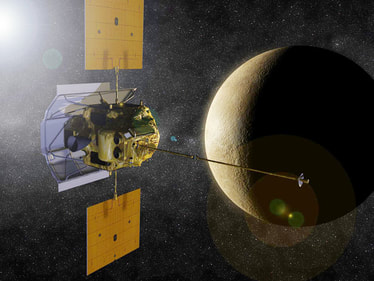
Shadows exist in space, too. MESSENGER is a NASA spacecraft on its way to study Mercury. Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. The scientists who built MESSENGER wanted to make sure it wouldn't get too hot. So they covered the side that faces the sun with a large piece of fabric. The fabric is called a "sunshade." It feels like a hard cloth. It makes a shadow by blocking the sun's light. This shadow keeps the spacecraft cool.
Click on the link below to participate in an interactive that explains how this works.
EXPLORING THE SCIENCE OF SHADOWS
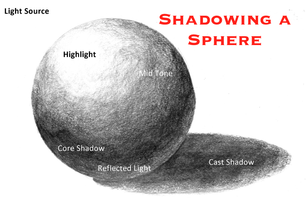
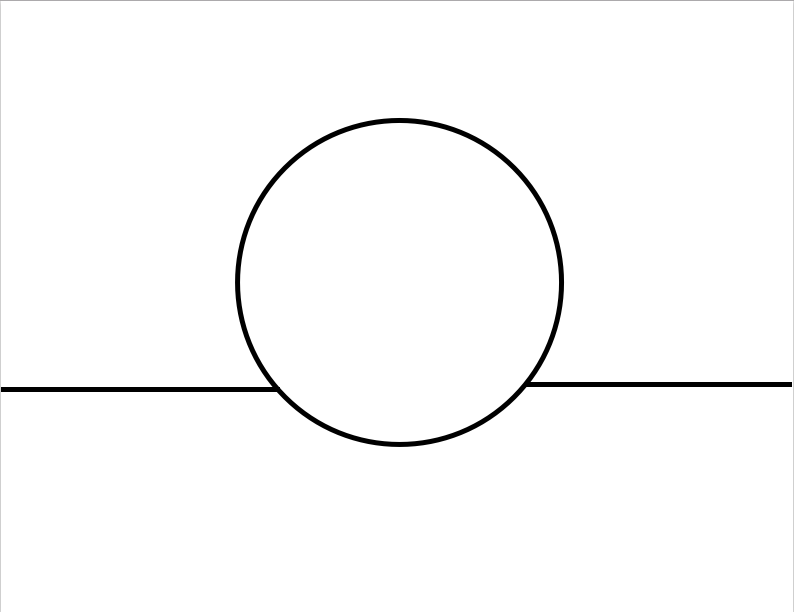
Now that you understand how light, darkness, and shadows work, let's see if you can show you understand by learning to draw shadowing on a sphere. Follow along as Mrs. Scott demonstrates this. Listen to her instructions. If you would like to practice at home, you can click on the icon below to watch a youtube tutorial on how to do this.
This is the template you will receive in class to practice shadowing. I embedded it here for you to print out at home if you want to practice.
END OF LESSON MODULE 1
Congratulations! You have finished The Lesson 1 Module of Gallery Enrichment.